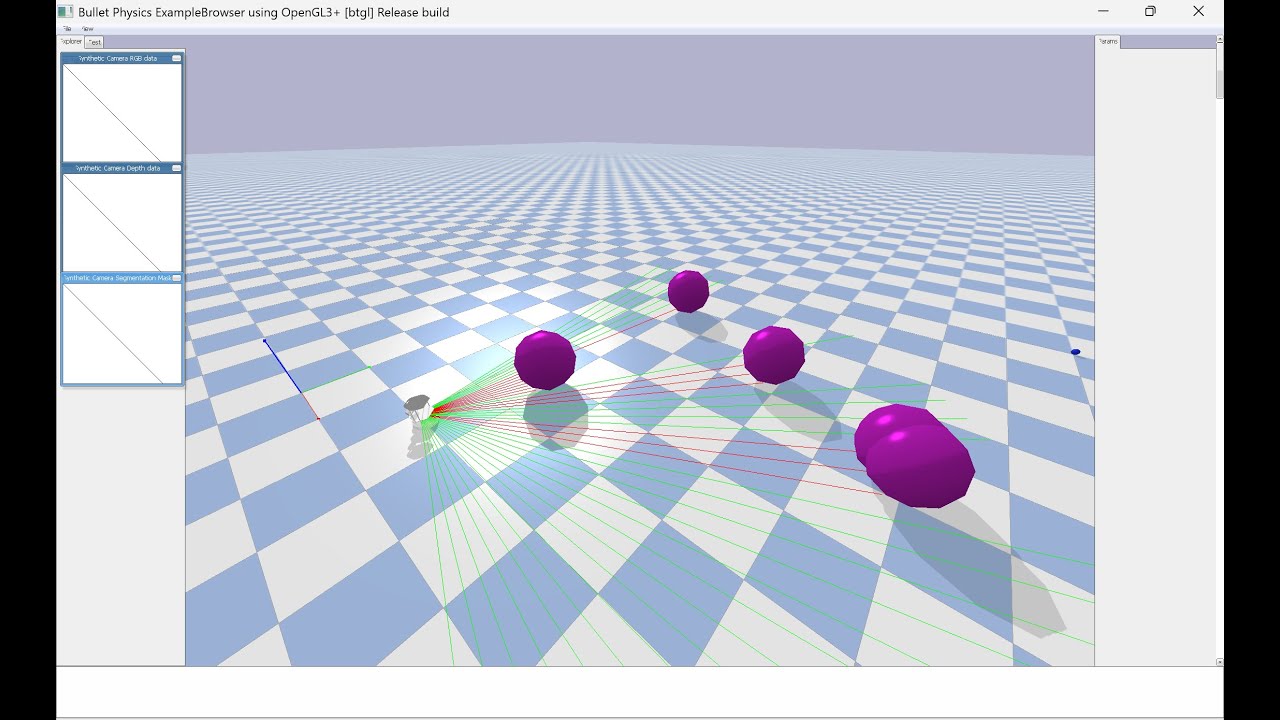
This project simulates a robot navigating towards a target while avoiding dynamic obstacles using the Pure Pursuit Method for path following and Vector Field Histogram (VFH) for obstacle avoidance.
This simulation demonstrates:
-
Pure Pursuit Path Following
The robot calculates the angle toward the target and adjusts its orientation accordingly to follow the path. -
Vector Field Histogram (VFH) Obstacle Avoidance
The robot scans its environment to detect nearby obstacles, generating a histogram of distances within its field of view. When obstacles are detected within a certain threshold distance, the robot adjusts its orientation to avoid them. -
Dynamic Obstacles
Obstacles move randomly, adding complexity to the robot's navigation task.
- Dynamic Targeting: The robot continuously re-orients toward a target position.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Upon detecting obstacles, the robot selects a safe angle to prevent collisions.
- Real-time Plotting: The simulation visually represents the robot, target, obstacles, and sensor beams.
- Polar Histogram Display: An inset plot shows the polar histogram of obstacle distances.
Kinematics.Control.mp4
Model of a differential-drive mobile robot, using wheel angular velocities, body velocities, and pose representation

Robot pose at time step i is:
Where:
- xi,yi: robot position in global frame.
- ψi: robot orientation (heading).
Time derivative:
The control inputs are wheel angular velocities:
Where:
- θ˙iR: right wheel angular velocity
- θ˙iL: left wheel angular velocity.
Distance between wheels:
- d: wheelbase
Robot linear and angular velocities are expressed as:

Where:
- vi: robot linear velocity
- wi: robot angular velocity
To compute the wheel angular velocities from robot velocities:

Mapping from robot velocity in body frame to global coordinates:

the global motion is:
- x˙i: vi cos ψi
- y˙i: vi sin ψi
- ψ˙i: wi